What is a monologue

A monologue is a long speech made by a single person in a play, movie, or other performance. It can also refer to a similar speech given in real life, such as a political or motivational speech. In literature, a monologue is a long speech made by a single character, in which the character expresses thoughts, feelings, or ideas. It is a way to explore the inner thoughts and emotions of a character and reveal information about the plot. It is a powerful tool used by playwrights, screenwriters, and other writers to reveal the inner thoughts and emotions of a character. It is a way for the audience to gain insight into the character’s minds and understand their motivations and actions. Monologues can also be used to reveal information about the plot, such as past events or plans. In literature, monologues can be found in plays, short stories, novels, and poetry. In plays and movies, monologues are usually delivered by actors on stage or screen, and they can be either dramatic or comedic in nature.
Monologues can be categorized into different types such as:
- Soliloquy: a monologue where a character speaks their thoughts out loud when they are alone. It’s a way to reveal the character’s inner thoughts and feelings.
- Asides: a monologue directed to the audience and not to the other characters on stage. It’s a way to reveal information to the audience that the other characters on stage are not aware of.
- Monologue of Action: where the character performs an action while speaking, which reinforces the message or emotion of the monologue.
Monologues are also used in public speaking, where a person delivers a speech to an audience. These can be motivational speeches, political speeches, or speeches given at special events. The purpose of a monologue in public speaking is to inform, inspire, or persuade the audience. Overall, monologues are an effective way for writers and speakers to convey information, reveal characters, and move the plot forward in an engaging way.
How to structure monologue
Monologues can be structured in different ways, depending on the purpose of the monologue and the style of the writer or speaker. However, here is a general structure that can be used as a guide:
- Introduction: The opening of the monologue should grab the audience’s attention and set the tone for the rest of the speech. This can be done through a strong opening line, a rhetorical question, or a surprising statement.
- Body: The body of the monologue is where the main message or point is delivered. This can be done through a series of short points or a longer narrative. The body should be well-organized and easy for the audience to follow.
- Climax: The climax is the most intense or emotional part of the monologue. This is where the character or speaker’s feelings and thoughts come to a head and the audience experiences the most impact.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should tie everything together and leave a lasting impression on the audience. This can be done through a call to action, a final message, or a memorable quote.
- Subtext: Subtext is the underlying meaning or message that is not spoken but is implied. The subtext is the most important element of the monologue, it is what makes the monologue truly powerful.
Keep in mind that this structure is a general guide, and not all monologues will fit perfectly into this format. Some monologues may have a different structure, depending on the style of the writer or speaker, or the purpose of the monologue. Ensure that the monologue is rehearsed and practiced to ensure that the delivery is natural and effective, and also to make sure that it is timed well and that it fits the context of the scene or play.
Tips for writing a monologue
Here are the tips for writing a monologue;
- Define the purpose: Before writing the monologue, it’s important to understand the purpose of the monologue. Is it meant to reveal a character’s thoughts and emotions? Is it meant to convey information or advance the plot? Knowing the purpose of the monologue will help you structure it and choose the right words and tone.
- Choose the character: Select the character who will be delivering the monologue. This will help you to understand the character’s motivations, thoughts, and emotions, which will help you to write the monologue.
- Brainstorm: Make a list of the key thoughts and emotions that the character is feeling, and the key information that needs to be conveyed. This will help you to organize the monologue and ensure that all the important points are covered.
- Write the introduction: The introduction should grab the audience’s attention and set the tone for the rest of the monologue. Use a strong opening line, a rhetorical question, or a surprising statement.
- Write the body: The body of the monologue is where the main message or point is delivered. Organize the key thoughts and emotions into a logical structure, and use descriptive language to help the audience understand and empathize with the character.
- Write the climax: The climax is the most intense or emotional part of the monologue. This is where the character’s feelings and thoughts come to a head and the audience experiences the most impact. Use powerful language and descriptive imagery to create an emotional impact.
- Write the conclusion: The conclusion should tie everything together and leave a lasting impression on the audience. Use a call to action, a final message, or a memorable quote to end the monologue.
Remember to proofread and rehearse your monologue to ensure it’s polished and effective.
What is a dialogue
Dialogue is a conversation between two or more characters in a play, movie, book, or another form of literature or media. It is used to reveal information about the characters, advance the plot, and create tension and conflict. In literature, dialogue is written in quotation marks and often includes stage directions, such as actions and descriptions of facial expressions, to help the reader visualize the scene. In plays and movies, dialogue is spoken by the actors on stage or screen. In literature, dialogue can be found in plays, short stories, novels, and poetry. Dialogue is an important tool for writers, as it allows them to reveal information about the characters and the plot, create tension and conflict, and advance the story. Dialogue can also be used to reveal a character’s personality, motivations, and thoughts. It also allows the audience to feel like they are part of the conversation and it can create a sense of realism. In addition to that, dialogue can be used to reveal the relationship between characters, their culture, and their social status. It also serves as a way of revealing the setting, context, and atmosphere of the scene.
What is an example of a monologue
Here’s an example of a dramatic monologue from a play:
Character: Isabella (from William Shakespeare’s “Measure for Measure”)
Setting: Isabella is a young nun pleading with Angelo, a powerful Duke, to spare her brother’s life.
Monologue:
“Oh, just judge!
If you have the power to redeem him thither,
And yet delay the punishment of,
Which is the course of justice! for thy power
Hangs in the even balance with thy justice
Severe in youthful hearts sometimes doth blunt
The edge of mercy. O, great duke, no more!
Look, whether you have mercy in your eye,
That such an arm as this, so wasted, thin,
That can scarce hold a bowl of water steady,
And yet to provoke, should here come in
To where I live, and end it in the sight
Of such a ghost as I am!”
This monologue reveals Isabella’s desperation and her strong sense of justice. It also uses powerful imagery to convey her emotional state.
What is the definition of a monologue
A monologue is an extended speech delivered by a single person. It can happen in a few different contexts;
- Drama: In plays and films, a monologue is a speech a character gives alone, expressing their thoughts, feelings, or motivations, often directly to the audience (known as a soliloquy) or to another character who isn’t responding.
- Performance: Stand-up comedians will often perform a monologue as part of their routine.
- Real life: More casually, a monologue can refer to a long, one-sided conversation where one person dominates the talking.
The word “monologue” comes from the Greek words “monos” (alone) and “legein” (to speak), so it literally means “speaking alone.”
Is a monologue just a speech
A monologue is a type of speech, but there’s a key difference;
- Speech: A general term for any spoken communication. It can be short or long, one-sided, or a conversation between multiple people.
- Monologue: A specific type of speech delivered by a single person for an extended period. It often has a dramatic purpose, revealing the character’s thoughts, feelings, or motivations.
So, all monologues are speeches, but not all speeches are monologues.
What are the 3 types of monologue
Here are 3 common types of monologues;
- Soliloquy: This is a monologue where a character speaks their thoughts aloud while alone on stage. The audience gets a window into the character’s inner world, their hopes, fears, and motivations. Soliloquies are classic elements of dramatic plays, like Hamlet’s famous “To be or not to be” speech.
- Dramatic Monologue: This is a broader term for a monologue delivered by a character, but not necessarily alone. The character might be addressing another character who isn’t responding, or they could be speaking directly to the audience. Dramatic monologues are often used to reveal the character’s backstory, personality, or turning point in their journey.
- Interior Monologue: This type of monologue doesn’t appear in spoken form, but rather in literature. An interior monologue represents the character’s internal thoughts and feelings, a stream of consciousness that gives the reader direct access to the character’s mind. It’s a common tool used by authors to create a deeper connection between the reader and the character.
What are the 4 things that make a good monologue
Here are 4 things that make a good monologue;
- Compelling Hook: A strong opening grabs the audience’s attention and makes them want to listen. This could be a surprising statement, a question, or a vivid image that sets the stage for the monologue.
- Clear Point of View: The monologue should showcase a strong perspective. What is the character trying to convey? What are their emotions and motivations? A good monologue reveals something important about the character’s inner world.
- Emotional Arc: A captivating monologue takes the audience on a journey. It might start with one emotion and build to another, or it could explore a range of feelings throughout. This emotional arc keeps the listener engaged and invested in the character’s plight.
- Vivid Language: Effective monologues use strong language to paint a picture and evoke emotions. This could involve figures of speech, sensory details, or powerful verbs that bring the character’s thoughts and experiences to life.
What three things must a monologue have
A good monologue can have many elements that make it strong, there are three essential ingredients;
- Single Speaker: By definition, a monologue requires a single person to deliver the speech. This is what distinguishes it from a dialogue or conversation between multiple people.
- Extended Speech: A monologue isn’t just a quick sentence or two. It’s an extended speech where the character has the opportunity to develop their thoughts and ideas.
- Dramatic Purpose: A monologue serves a dramatic purpose. It’s not just a random collection of words. It’s used to reveal the character’s inner self, motivations, backstory, or a turning point in their journey. It moves the plot or character development forward in some way.
What does a good monologue look like
A good monologue looks like a miniature drama in itself. Here’s a breakdown of what it might look like;
Structure
- Hook (Beginning): The first lines grab the audience’s attention. This could be a question, a surprising statement, or a vivid image that sets the scene. Imagine it as the opening line of a story that makes you want to hear more.
- Body (Middle): This is the heart of the monologue where the character’s thoughts and emotions unfold. It might explore a conflict, a memory, a turning point, or a secret desire. A good monologue will have a clear point of view and an emotional arc, taking the listener on a journey.
- Resolution (Ending): The monologue concludes, leaving the audience with a sense of closure or a new understanding of the character. This doesn’t necessarily mean a happy ending, but it should feel complete.
Content
- Character Revelation: A strong monologue reveals something important about the character’s inner world. What are their motivations, fears, or desires? The audience should gain a deeper understanding of who this person is.
- Vivid Language: The monologue uses strong verbs, imagery, and figurative language to paint a picture and evoke emotions. This could involve metaphors, similes, or sensory details that bring the character’s thoughts and experiences to life.
Performance
- Delivery: A good monologue is delivered with conviction and emotional depth. The speaker should use vocal variety, pacing, and gestures to bring the character’s words to life. Imagine an actor embodying the character and truly feeling the emotions they express.
Here’s an analogy: Think of a monologue like a song with one singer. It has a beginning, middle, and end, a clear point of view, and an emotional arc that keeps the listener engaged. The strong lyrics (language) are delivered with powerful vocals (performance) to create a memorable experience.
What are some good monologue ideas
Here are some monologue ideas that you can explore depending on the tone and genre you’re looking for;
Dramatic
- A soldier returning home from war struggles to reconnect with their family.
- A doctor wrestles with a life-or-death decision.
- A grieving parent addresses an empty chair, remembering a lost child.
- A villain reveals their twisted motivations to the hero they’ve captured.
Comedic
- A stagehand accidentally gets thrust into the spotlight and has to improvise.
- A robot malfunctions and starts hilariously questioning its existence.
- A conspiracy theorist tries to convince a stranger of their outlandish beliefs.
- A chef delivers a passionate (and possibly nonsensical) monologue about the importance of a perfectly cooked egg.
Reflective
- A forgotten toy reflects on its purpose and place in the world.
- A time traveler ponders the consequences of changing the past.
- A mirror delivers a monologue about the reflections it has seen over the years.
- A painting comes alive and expresses its frustration at being confined to the canvas.
These are just a few starting points, you can also consider;
- Genre twists: Put a comedic spin on a typically dramatic scenario, or vice versa.
- Unique perspectives: Try a monologue from the viewpoint of an inanimate object, an animal, or even an abstract concept like time.
- Social commentary: Use a monologue to explore a relevant social issue through a character’s lens.
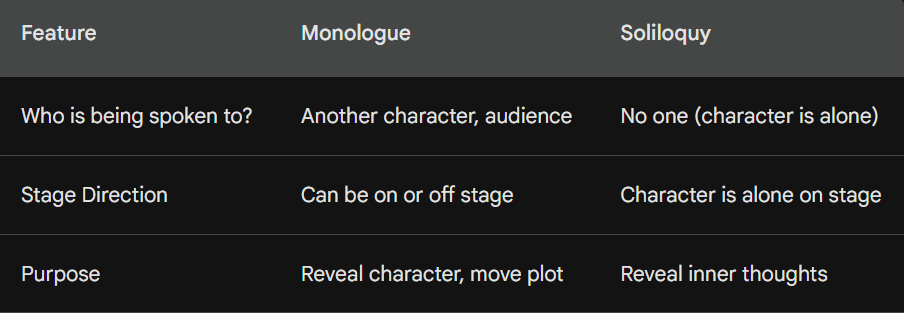
What is a monologue vs soliloquy
A monologue and a soliloquy are both extended speeches by a single person, but there’s a key difference in who the character is speaking to:
- Monologue: A general term for a speech delivered by one person at length. This can happen in various contexts:
-
- Drama: A character speaks to another character or the audience directly.
- Performance: Stand-up comedians or storytellers might perform a monologue as part of their act.
- Real life: A long, one-sided conversation where one person dominates the talking.
- Soliloquy: A specific type of monologue where a character speaks their thoughts aloud while alone on stage. The audience gets a direct window into the character’s inner world, their hopes, fears, and motivations. Soliloquies are classic elements of dramatic plays, like Hamlet’s famous “To be or not to be” speech.
Here’s a table to summarize the key differences;
Can a monologue be talking to someone
Yes, a monologue can be talking to someone! This is the most common type of monologue.
The term “soliloquy” refers specifically to a monologue where a character speaks their thoughts aloud while alone on stage. So, any monologue where the character is addressing another character (or the audience) falls under the broader category of just a “monologue.” Here are some examples of monologues directed at someone else;
- A lover pouring their heart out to their partner
- A parent delivering a heartfelt message to their child
- A villain taunting their defeated opponent
- A lawyer making a closing argument to a jury
These monologues can be just as powerful and revealing as soliloquies. They allow the character to express their emotions and motivations directly to another person, creating dramatic tension and driving the plot forward.
How do you judge a monologue
Here are some key aspects to consider when judging a monologue;
Content
- Clarity and Focus: Does the monologue have a clear purpose and a central idea? Is it easy to understand what the character is trying to convey?
- Character Development: Does the monologue reveal something important about the character’s inner world? Their motivations, fears, desires, or backstory?
- Emotional Arc: Does the monologue take the listener on a journey? Does it explore a range of emotions or build to a particular climax?
- Originality: Is the concept or perspective unique and engaging? Does it stand out from typical monologues?
Delivery
- Vocal Variety: Does the speaker use changes in pitch, volume, and pace to keep the audience engaged?
- Clarity: Is the monologue easy to understand? Does the speaker enunciate clearly and project their voice?
- Body Language: Do the speaker’s gestures and facial expressions complement the words and emotions being conveyed?
- Stage Presence: Does the speaker command the stage and connect with the audience?
Overall Impact
- Engagement: Did the monologue hold your attention? Were you invested in the character and their story?
- Memorable: Did the monologue leave a lasting impression? Did it make you think or feel something?
- Effectiveness: Did the monologue achieve its purpose? Did it reveal the character effectively or move the story forward (if applicable)?
Here are some additional factors to consider depending on the context;
- Competition: If judging a monologue competition, consider any specific criteria or themes.
- Genre: A comedic monologue might have different expectations than a dramatic one.
- Performance Level: For beginners, focus on basic elements like clarity and memorization. For advanced actors, consider more nuanced aspects like emotional depth and character embodiment.
Can other characters hear a monologue
There are two main types of monologues to consider:
- Monologue: This is the broader term for a speech delivered by one person at length. In this case, other characters can hear the monologue if they are present in the scene.
- For instance, a dramatic monologue might involve a character pleading with another character, delivering a passionate speech to a group, or even confronting a villain.
- Soliloquy: This is a specific type of monologue where a character speaks their thoughts aloud while alone on stage. Here, other characters are not present and therefore cannot hear the monologue. The soliloquy allows the audience a direct window into the character’s inner world.
So, to answer your question directly;
- If it’s a monologue, other characters can hear it if they are present in the scene.
- If it’s a soliloquy, other characters cannot hear it as the character is alone.
Can a monologue be unspoken
In the strictest sense, a monologue is a spoken speech by a single person. The word itself comes from the Greek words “monos” (alone) and “legein” (to speak).
However, there is a concept related to monologues that can be unspoken;
Internal Monologue: This refers to the “stream of consciousness” or the constant flow of thoughts and unspoken words that occur in our minds. It’s the voice we hear “inside our heads” narrating our thoughts and feelings. While not technically a monologue because it’s not spoken aloud, internal monologues are a literary device used by authors to give readers direct access to a character’s inner thoughts and motivations. This can be a powerful tool for character development and building a connection with the reader. So, while unspoken monologues don’t exist in the traditional sense, the concept of an internal monologue is a close relative that plays a significant role in storytelling.
Can a monologue be in your head
No, a monologue in your head wouldn’t be considered a true monologue. Here’s why;
- Monólogo vs. Internal Monologue: The word “monologue” comes from Greek, meaning “alone” (monos) and “speaking” (legein). So by definition, a monologue requires spoken words, even if delivered to oneself.
- Internal Experience: An internal monologue, the voice you hear in your head narrating your thoughts, is a common human experience. It’s not a spoken speech, but rather an internal processing of thoughts and feelings.
- Focus on Delivery: Monologues have a dramatic purpose. They are delivered to reveal a character’s inner world, and motivations, or move the plot forward in a story. An internal monologue doesn’t have this external focus.
Here’s an analogy: Think of a monologue as a song with one singer. It requires an outward performance, even if to oneself. An internal monologue would be more like the unspoken thoughts and feelings that inspire the lyrics of the song. Internal monologue might sound like a monologue in your head, but it doesn’t fulfill the key aspects of a true monologue: spoken delivery and a dramatic purpose.
Can two people do a monologue
No, a monologue cannot involve two people speaking at the same time. A monologue is a speech delivered by a single person for an extended period. However, there are a few workarounds or related concepts that might be what you’re looking for;
- Duologue: If you want two characters to speak but not necessarily have a conversation, you could consider a duologue. This is a conversation between two people, but it could be structured in a way where each person delivers a long, uninterrupted speech.
- Alternating Monologues: Another option is to write or perform alternating monologues. Here, each character delivers their monologue one after another, focusing on their thoughts and experiences. This can create an interesting back-and-forth dynamic and reveal different perspectives on a shared situation.
- Split Monologue: This is a less common approach, but you could explore a “split monologue” where two characters seem to share a single internal monologue. This could be used to represent conflicting emotions or inner struggles within one character. However, it’s important to differentiate the voices and perspectives to avoid confusion.
- Dramatic Scenes with Limited Dialogue: Plays and films can have scenes where two characters are present but there’s minimal conversation. One character might deliver a long, emotional speech while the other listens and reacts non-verbally. This can be a powerful way to showcase one character’s thoughts and feelings.
While none of these options are technically monologues involving two people speaking simultaneously, they offer ways to achieve a similar effect or explore a situation from multiple perspectives using extended speeches.
Why are monologues destructive in relationships
Monologues themselves aren’t inherently destructive in relationships. They can be a healthy part of communication if used correctly. However, frequent or one-sided conversations where one person dominates can be harmful to a relationship. Here’s why;
- Lack of Mutuality: A healthy relationship is a two-way street. Monologues prevent a true conversation from happening. The person listening isn’t given the space to share their thoughts and feelings, leading to a feeling of being unheard and unimportant.
- Disengagement: If one person constantly talks, the other person might eventually tune out or withdraw from the conversation altogether. This creates a disconnect and makes it difficult to build intimacy and understanding.
- Frustration and Resentment: The person who isn’t being heard might feel frustrated and resentful. Their needs and feelings are being pushed aside, which can damage the emotional foundation of the relationship.
- Problem-solving Difficulties: Relationships involve give and take. If both partners can’t voice their concerns and perspectives, it becomes difficult to solve problems or make decisions together.
Here are some tips for healthy communication that avoids monologue pitfalls;
- Active Listening: Pay attention to what your partner is saying, both verbally and nonverbally. Try to understand their perspective before responding.
- Take Turns Talking: Create space for both partners to share their thoughts and feelings.
- Ask Open-Ended Questions: Encourage your partner to elaborate and share their experiences.
- Validate Their Feelings: Acknowledge and show empathy for your partner’s emotions, even if you don’t agree with everything they say.
How rare is an inner monologue
Studies suggest that inner monologues are not as common as we might think. Here’s a breakdown;
- Prevalence: Research by psychologist Russell Hurlburt estimates that between 30% and 50% of people report experiencing regular inner monologues.
- Individual experiences: Some people describe a constant stream of internal narration, while others have thoughts that are more visual or emotion-based. There’s a spectrum of inner experience.
- Not a sign of abnormality: Having or not having an inner monologue isn’t a sign of intelligence or mental health issues. It’s simply a different way of thinking.
Here are some things to consider;
- Thinking Styles: People who don’t experience a verbal inner monologue might think in images, emotions, or a combination.
- Focus on the Present: Some people might be more present-moment-focused, experiencing the world directly without internal commentary.
- Cultural Differences: There might be cultural influences on how people think. Some cultures might emphasize more analytical thinking styles.
Inner monologue vs. problem-solving: It’s important to distinguish between an inner monologue and internal thought processes used for problem-solving or decision-making. Everyone engages in some form of internal mental processing.
What is a one-sided conversation called
A one-sided conversation can be called a few things, depending on the context;
- Monologue: This is the most general term for a speech delivered by a single person for an extended period. It can happen in various contexts, but it doesn’t necessarily imply a negative connotation.
- Harangue: This refers to a long, angry speech that is often critical or accusatory. It emphasizes the negative and forceful nature of the one-sided conversation.
- Tirade: Similar to a harangue, a tirade is a long, angry, or emotional outburst.
- Rant: This is another term for a long, angry speech, often on a specific topic. It can be less intense than a harangue or tirade.
- Talking at someone: This is a more informal way to describe a one-sided conversation where the listener isn’t being heard or isn’t able to get a word in.
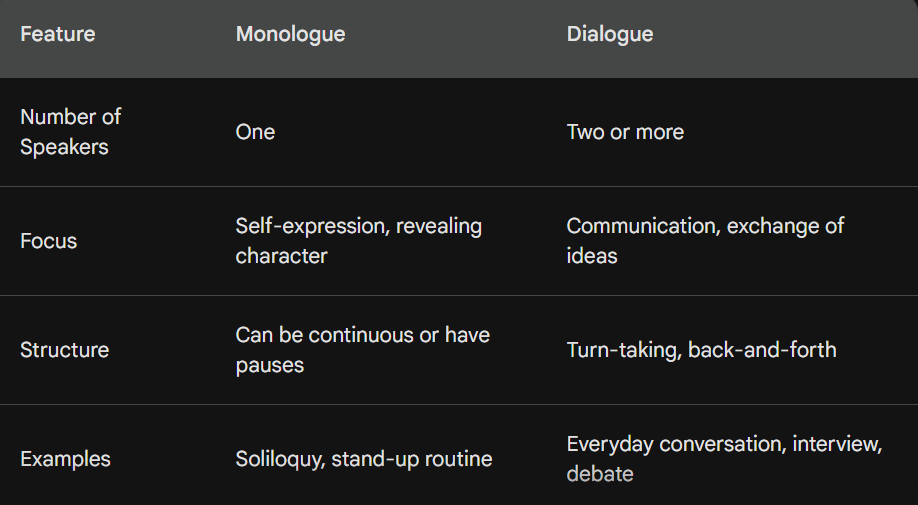
How does a monologue differ from a dialogue
The key difference between a monologue and a dialogue lies in the number of speakers involved;
- Monologue: A monologue is an extended speech delivered by one person. It can be dramatic (revealing a character’s inner thoughts or motivations) or casual (someone dominating a conversation).
- Dialogue: A dialogue is an exchange of words involving two or more individuals. It involves an exchange of thoughts and ideas, with each person taking turns speaking and listening.
Here’s a table summarizing the core differences;
Additional Points
- Internal Monologue: While not technically a monologue because it’s unspoken, an internal monologue is the constant flow of thoughts within a person’s mind. This is a literary device used by authors to reveal a character’s inner world.
- Dominating Conversations: A seemingly balanced conversation can turn into a monologue if one person talks excessively without giving the other a chance to respond. This can be a communication issue.
What are the key characteristics of a monologue
Here are the key characteristics of a monologue;
Speaker and Delivery
- Single Speaker: By definition, a monologue has only one person delivering the speech.
- Extended Speech: It’s not a quick sentence or two, but a sustained period where the character has the opportunity to develop their thoughts and ideas.
- Delivery: A strong monologue is delivered with conviction and emotional depth. The speaker should use vocal variety, pacing, and gestures to bring the character’s words to life (if applicable).
Content and Purpose
- Dramatic Purpose: A monologue serves a dramatic purpose in storytelling or communication. It’s not just a random collection of words. It’s used to;
- Reveal Character: A strong monologue reveals something important about the character’s inner world. This could be their motivations, fears, desires, backstory, or a turning point in their journey.
- Move the Plot Forward (if applicable): In plays or films, a monologue can advance the plot by revealing crucial information or setting the stage for future events.
Content and Focus
-
- Clarity and Focus: Does the monologue have a clear purpose and a central idea? Is it easy to understand what the character is trying to convey?
- Emotional Arc: Does the monologue take the listener on a journey? Does it explore a range of emotions or build to a particular climax?
Additional characteristics to consider;
- Language: Effective monologues use strong verbs, imagery, and figurative language to paint a picture and evoke emotions.
- Soliloquy vs. Monologue: A soliloquy is a specific type of monologue where a character speaks their thoughts aloud while alone on stage. Monologues can be directed at another character or the audience.
What are the different types of monologues commonly found in literature and drama
In literature and drama, there are two main categories of monologues, along with a special unspoken type used in literature;
- Dramatic Monologue: This is the most common type encountered. It features a single character delivering an extended speech, often directly addressing another character or the audience.
- Soliloquy: This is a specific type of monologue where a character speaks their thoughts aloud while alone on stage. The audience gains a direct window into the character’s inner world, their hopes, fears, and motivations. Soliloquies are classic elements of dramatic plays, like Hamlet’s famous “To be or not to be” speech.
How is a monologue used in storytelling and performance?
Monologues play a vital role in storytelling and performance by offering unique ways to develop characters, move plots forward, and connect with the audience. Here’s a breakdown of their functions;
Character Development
- Inner World Revelation: Monologues allow characters to express their deepest thoughts, feelings, motivations, and desires. This can be especially useful for complex characters or situations where dialogue wouldn’t reveal everything.
- Backstory Exposition: A monologue can efficiently deliver a character’s backstory, explaining their past experiences and shaping their current actions.
- Emotional Arc: Monologues can showcase a character’s emotional journey, tracing their feelings of anger, frustration, joy, or despair. This creates a more well-rounded and relatable character.
Plot Development
- Exposition: Monologues can provide crucial information about the setting, characters, or plot points that might not be easily revealed through dialogue.
- Turning Point: A monologue can mark a turning point in the story, where a character makes a decision, realizes something important, or experiences a shift in perspective.
- Building Suspense: A well-crafted monologue can build suspense by hinting at future events, foreshadowing conflicts, or creating a sense of mystery.
Audience Connection
- Direct Address: Monologues spoken directly to the audience can break the fourth wall and create a sense of intimacy. The audience feels like they’re getting a secret glimpse into the character’s soul.
- Emotional Impact: A powerful monologue can evoke strong emotions in the audience, making them feel empathy, sympathy, or even fear for the character.
- Humor and Entertainment: Monologues can also be used for comedic effect, delivering jokes, observations, or witty remarks to entertain the audience.
Performance Applications
- Stand-up Comedy: Comedians often use monologues as part of their routine, delivering funny observations or stories.
- Dramatic Performances: Monologues are a staple of dramatic acting, allowing actors to showcase their range and skill in portraying a character’s emotions.
- Audition Pieces: Actors often use monologues as audition pieces to showcase their talent to casting directors.
What is the purpose of delivering a monologue in various contexts such as theater, film, or literature
The purpose of a monologue can vary depending on the context, but here’s a breakdown of its common uses in theater, film, and literature;
In Theater
- Character Development: A monologue allows a character to reveal their inner thoughts, motivations, and desires directly to the audience. This can be especially helpful for complex characters or situations where dialogue wouldn’t be enough. (Think of Hamlet’s “To be or not to be” soliloquy revealing his internal struggle.)
- Emotional Connection: The direct address of a monologue can create a feeling of intimacy with the audience. They get a deeper understanding of the character’s emotional state, fostering empathy or connection.
- Plot Exposition: Monologues can be used to efficiently deliver backstory or crucial information that might not be easily revealed through dialogue. This can establish the setting, introduce characters, or set the stage for future events.
- Shifting the Narrative: A monologue can mark a turning point in the story. The character might make a decision, have a realization, or experience a change in perspective - all revealed through their internal monologue.
- Building Suspense: Well-crafted monologues can create suspense by hinting at future conflicts, foreshadowing events, or leaving the audience with unanswered questions.
In Film
Many of the purposes of theater apply to film as well. However, the film offers some additional possibilities;
- Visual Storytelling: Filmmakers can use visuals alongside the monologue to enhance its impact. Think of flashbacks or dream sequences triggered by the character’s words.
- Interior Monologue (Voiceover): In some cases, a monologue might be delivered as a voiceover, representing the character’s unspoken thoughts. This allows for a more subjective and intimate perspective.
- Breaking the Fourth Wall: Similar to theater, film monologues can break the fourth wall by having the character directly address the camera, creating a sense of intimacy with the audience.
In Literature
- Internal Monologue: This unspoken monologue gives readers direct access to a character’s inner thoughts and feelings. This can be a powerful tool for character development and building a connection with the reader. (Think of stream-of-consciousness techniques in novels.)
- Character Revelation: Similar to theater and film, monologues can reveal a character’s motivations, backstory, or emotional state. This can be done through the character’s internal monologue or their spoken words directed at another character.
- Plot Development: Authors can use monologues to reveal crucial information or move the plot forward. This might involve backstory exposition, foreshadowing future events, or showcasing a character’s decision-making process.
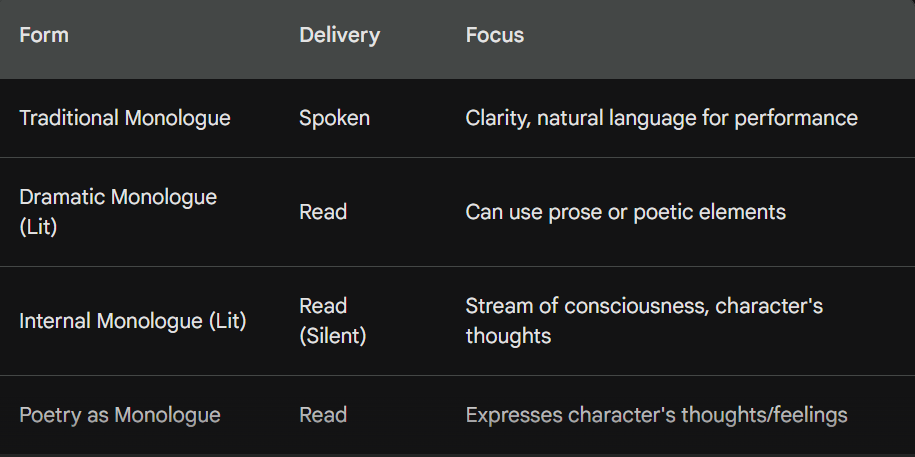
Can a monologue be written in different forms, such as prose or poetry
A monologue can be written in different forms, though the traditional delivery is spoken language. Here’s a breakdown of how monologues can appear in different forms;
Traditional Monologue (Drama/Performance): This is the most common form, where a character delivers a speech in a play, film, or performance. It’s written in prose, focusing on clarity and natural language for the actor to deliver convincingly.
Dramatic Monologue (Literature): This is a written monologue intended to be read, not necessarily performed. It can still use prose for a more conversational style, but it might also incorporate elements of poetry like figurative language or rhythmic structure to create a more emotional impact.
Internal Monologue (Literature): This unspoken monologue is written in prose and represents a character’s stream of consciousness or inner thoughts. It allows readers direct access to the character’s internal world. Authors use various techniques like stream-of-consciousness or free indirect discourse to achieve this effect.
Poetry as Monologue: While not as typical, a poem can take the form of a monologue. The entire poem is essentially the voice of one character expressing their thoughts and feelings. This can be done in various styles, from dramatic monologues to sonnets or even free verse.
Here’s a table summarizing the key points;
What techniques are employed by writers and performers to create compelling monologues
Writers and performers use a variety of techniques to create compelling monologues that capture the audience’s attention and effectively reveal the character. Here are some key elements to consider;
Writing Techniques
- Strong Central Idea: A clear focus and purpose keep the monologue from rambling. What is the character trying to convey?
- Vivid Language: Using strong verbs, descriptive details, and figurative language like metaphors, similes, or personification helps paint a picture and evoke emotions in the audience.
- Emotional Arc: Does the monologue take the audience on a journey? Does it explore a range of emotions or build to a particular climax? This keeps the listener engaged.
- Character Revelation: A strong monologue reveals something important about the character’s inner world. What are their motivations, fears, desires, or secrets?
- Dialogue vs. Monologue: Even in a monologue, consider incorporating elements of dialogue or imagined responses from a silent character. This can create a sense of back-and-forth and make the monologue feel more dynamic.
Performance Techniques
- Vocal Variety: The speaker should use changes in pitch, volume, and pace to keep the audience engaged. Avoid monotony!
- Clarity: Enunciate clearly and project your voice so the audience can understand every word.
- Body Language: Use gestures, facial expressions, and posture to complement the words and emotions being conveyed.
- Stage Presence: Command the stage and connect with the audience through eye contact and confident delivery.
Additional Techniques
- Humor: Even in serious monologues, a touch of humor can be disarming and relatable.
- Suspense: Leaving the audience with unanswered questions or hinting at future events can pique their interest.
- Silence: Strategic pauses can add emphasis and allow the audience to absorb the weight of the character’s words.
- Props: For performances, a well-chosen prop can add depth and focus to the monologue.
How does the structure of a monologue contribute to its effectiveness in conveying emotions or ideas
The structure of a monologue plays a crucial role in conveying emotions or ideas effectively. Here’s how different structural elements contribute;
Overall Arc
- Clear Beginning, Middle, and End: A strong monologue, like any good story, needs a clear beginning that establishes the context and character, a middle that explores the emotional core and develops the central idea, and an end that leaves a lasting impression. This structure helps guide the audience through the character’s journey.
- Emotional Arc: The structure should reflect the emotional journey of the character. Does the monologue start with anger and build to acceptance? Does it begin with confusion and end with a newfound resolve? The structure should mirror this emotional shift, keeping the audience engaged.
Techniques and Pacing
- Shifting Pacing: Varying the pace of the monologue can emphasize important moments and build tension. Slow, deliberate delivery can convey deep emotions, while faster speech might reflect urgency or frustration.
- Repetition: Strategic repetition of words, phrases, or ideas can create emphasis, drive home a point, or showcase the character’s fixation on a particular issue.
- Juxtaposition: Contrasting ideas or images placed close together can create a powerful effect. For example, a character might talk about their happy childhood home right before revealing a traumatic event that shattered their sense of security.
- Silence: Well-placed pauses can be just as impactful as spoken words. Silence allows the audience to absorb the weight of what has been said and creates space for reflection.
Language and Style
- Figurative Language: Using metaphors, similes, and other figures of speech can add depth and emotional resonance to the monologue. Descriptive language helps the audience visualize the scene and connect with the character’s experience.
- Rhetorical Questions: Posing questions that don’t necessarily need answers can make the audience think and engage with the character’s perspective.
- Shifting Styles: A monologue can incorporate elements of dialogue, internal monologue, or even song or poetry depending on the desired effect. This keeps the delivery interesting and reflects the character’s emotional state.
Are there any notable examples of famous monologues in English literature or drama
English literature and drama are filled with famous monologues that have captivated audiences for centuries. Here are a few notable examples;
Shakespearean Speeches
- “To be or not to be” (Hamlet): This iconic soliloquy from Hamlet explores themes of life, death, and mortality.
- “What a piece of work is a man!” (Hamlet): This soliloquy reveals Hamlet’s contemplation of human nature and his struggle for revenge.
- “Friends, Romans, countrymen, lend me your ears” (Julius Caesar): Mark Antony’s famous funeral oration sways public opinion in Caesar’s favor.
- “The quality of mercy is not strain’d” (The Merchant of Venice): Portia’s plea for mercy highlights themes of justice and forgiveness.
Other Classics
- “O Captain! My Captain!” (Walt Whitman): This poem is a moving elegy lamenting the death of Abraham Lincoln.
- “All the world’s a stage” (As You Like It by William Shakespeare): Jacques' famous speech compares life to a performance.
- “I have a Dream” (Speech by Martin Luther King Jr.): This powerful speech outlines King’s vision for racial equality in America.
- “The horror! The horror!” (Heart of Darkness by Joseph Conrad): Marlow’s final words capture the psychological toll of colonialism.
- “I wandered lonely as a cloud” (William Wordsworth): This famous poem describes the speaker’s encounter with beautiful daffodils and the emotions it evokes.
Modern Monologues
- “Frankly, my dear, I don’t give a damn” (Gone With the Wind by Margaret Mitchell): Rhett Butler’s iconic line perfectly captures his cynical and detached personality.
- “Elementary, my dear Watson” (Sherlock Holmes by Arthur Conan Doyle): This famous phrase, though not strictly from a monologue, is synonymous with the brilliant detective Sherlock Holmes.
- “I am Groot” (Guardians of the Galaxy by James Gunn): While not a complex monologue, this simple phrase from Groot has become a pop culture phenomenon due to its emotional weight within the film’s context.